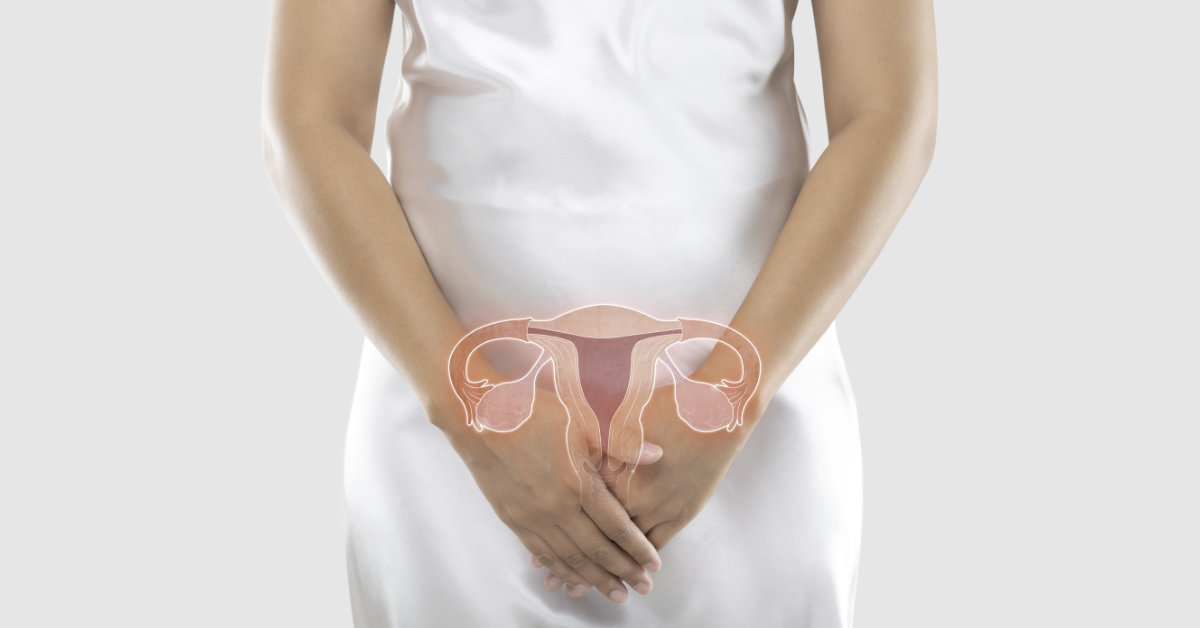
Polycystic Ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is a common condition where a woman’s ovary produces an excess amount of hormones, typically male hormones (androgens). It is very common, and reported to affect nearly 8% of all reproductive aged women in the world!
This surplus of androgens may cause you to have absent or irregular menstrual cycles, which can affect not only your fertility, but impact your overall health. Extended periods of time without a menstrual cycle raises the risk of having unpredictable heavy bleeding, as well as uterine cancer.
Beyond its effects on the menstrual cycle, PCOS can cause other bothersome symptoms such as acne, frontal hair loss or baldness and excess facial or body hair growth. These symptoms may be less noticeable in some individuals due to variations among hair and skin color and hair removal methods, but diagnostic blood tests assessing androgen levels can confirm the diagnosis as well.
Lastly, ultrasound findings showing multiple small ovarian follicles, often described as a “string of pearls”, contributes to the diagnosis of PCOS. Although ultrasound can be an important part of the criteria used to diagnose PCOS, this aspect can be confusing to interpret, because not everyone with a large number of ovarian follicles truly has PCOS. If you suspect PCOS or want to explore this further, I recommend you follow up with your OBGYN or a Reproductive Fertility specialist to discuss your symptoms and if this may affect your overall health and fertility.